Synteny comparison#
Method#
L. ferriphilum ML-04 and L. ferriphilum YSK, two strains having complete genome were selected for comparison. Their sequences were downloaded and decompressed. BLAST was used to make a database of my assembly and then produce crunch files for ACT to view comparison.
Command:
makeblastdb -in lfts.fasta -out lfts -dbtype nucl
blastn -query ml04.fna -out lfts_ml04.crunch -db lfts -outfmt 6
blastn -query ysk.fna -out lfts_ysk.crunch -db lfts -outfmt 6
-outfmt 6 is required for ACT
Results and discussion#
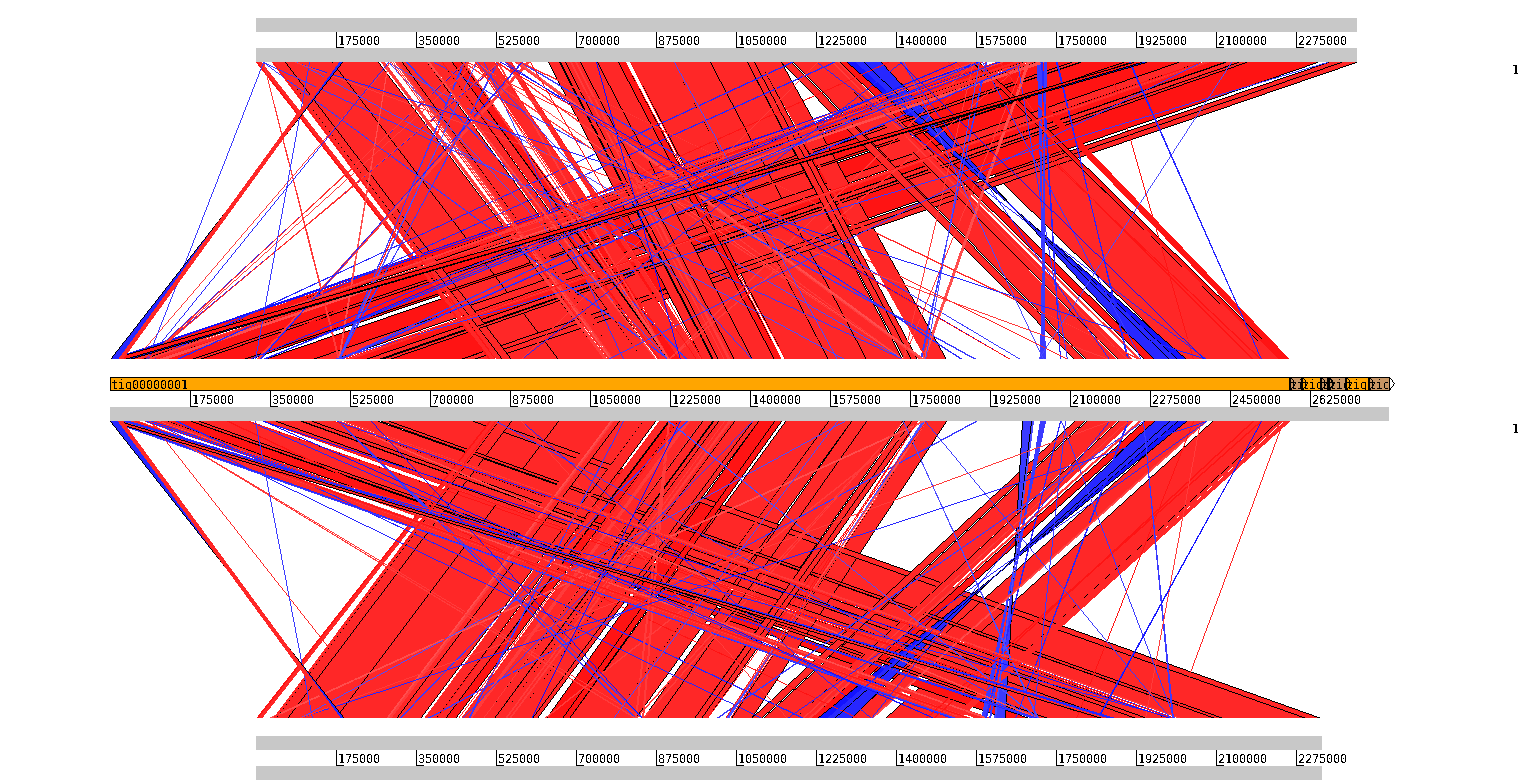 The sequence in the middle is my contigs.fasta. Considering the circular feature of the genome, the first contig aligns well with both ML-04 and YSK. The size of contig 1 is larger and a new region is presented.
The sequence in the middle is my contigs.fasta. Considering the circular feature of the genome, the first contig aligns well with both ML-04 and YSK. The size of contig 1 is larger and a new region is presented.
Q & A#
Homology search#
How relevant is the output format that you choose?
Different output formats are for different usages. Different software require different format to parse. As said above, ACT requires format 6 of BLAST+.
How do the resulting hits vary when you change the minimum e-value?
E-value represents the number of hits expected to see by chance when searching a database of a particular size. The lower the e-value, the more significant the match is. Decreasing minimum e-values generates less resulting hits.
How is the alignment score calculated?
It is calculated by summing the substitution score (base on substitution matrix) and gap scores (opening and extension penalties).
How important is the number of threads when you blast against a database, or against a particular sequence?
Increasing the number of threads to utilize parallel computation will increase the speed of search.